
ACL Digital
How IoT Solutions Help OEMs to Reduce Cost in the Aerospace Industry
The potential of IoT in the aviation industry is endless. By effectively utilizing IoT, the aviation industry can focus on increasing passenger safety, reducing cost, system maintenance, efficiency, security, and customer experience.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is already making its way into the aircraft cabin—helping the Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEM) to reduce the cost of the aircraft with smart aerospace industry solutions. Aircraft cabin electronics include monitoring & controlling a large number of interconnected and electrically powered equipment and subsystems of the cabin. These include cabin lights, passenger service units, window shades, smoke detection, fire extinguishing systems, air conditioning, overhead cabin audio, water systems, waste systems, flight attendant panel, and support of in-flight entertainment systems. The airlines and OEMs are looking to manage the cost of cabin electronics as these subsystems form a significant component of the overall cost of an aircraft. To achieve this, OEMs are developing IoT solutions to evolve the next-generation aircraft cabins at a reduced cost.
Why is an IoT-enabled aircraft cabin the need of the hour?
A large number of sensors and control switches are installed in the aircraft cabin systems. Most of these cabin subsystems have wired components, bringing severe aircraft system design and maintenance problems. The main drawbacks are as follows:
- Wired connections increase the wiring complexity, seriously affecting the design, installation, and debugging of these systems
- A large number of wires create difficulties in the maintenance of these aircraft systems
- The wires also contribute significantly to the aircraft’s weight, subsequently reducing fuel efficiency
- The wiring also occupies the space of the aircraft and makes the aircraft’s limited space narrow
Using wireless sensors and control mechanisms in the IoT world, the OEMs can significantly reduce the aircraft’s engineering design, installation, and maintenance cost.
How to design an IoT-enabled aircraft cabin subsystem?
The IoT-enabled aircraft cabin subsystem consists of three parts: end devices, mesh communication network, and information center. Thread technology based on 6LoWPAN, which, in turn, uses the IEEE 802.15.4 wireless protocol with mesh communication is composed of several end device nodes and a border router to form basic monitoring and controlling area and is located at the bottom of the system. The border router can also act as a gateway. The overall structure of the system is as shown in the below diagram.
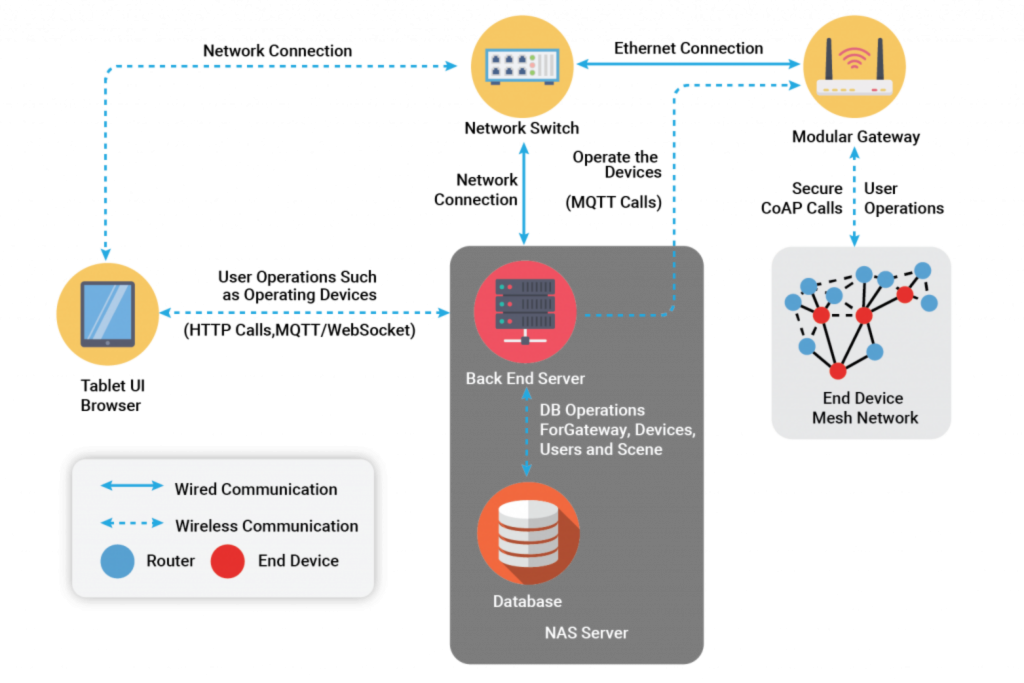
The end device can be configured with single or multiple different precision sensors and actuators used for the subsystem operation. End-device nodes are deployed in the monitoring and controlling area.
In a self-organizing way, the end-device node constitutes wireless sensor networks and cooperatively senses and collects network coverage areas. After the primary process of the detected information, monitoring information is relayed to the border router/gateway over a thread network. Subsequently, through the aircraft ethernet network, gateway nodes will send this information to a central monitor and controller. Finally, based on monitoring data of the sub-system, the controller will take integrated management and configuration of the end-device network.
Each end-device node can also be connected to some controlling mechanism like lights and LED indicators. The controller can perform any control operation on the device, which is first sent from the controller to the gateway over the aircraft’s ethernet network. The gateway then sends the control command to the end device over the Thread mesh network. The end devices receive the command and take appropriate action like turning the lights ON/OFF.
Any legacy aircraft subsystem like a cabin management system consists of sensors and actuators connected using wires to a central controller. A flight attendant panel is connected to the cabin management controller over Ethernet using the aircraft’s networking system. To upgrade this system to wireless, we can integrate low-power wireless MCUs with the sensor and actuators to communicate to an IoT gateway over RF protocols like Thread, BLE, or Zigbee. The cabin management system controller can communicate with the IoT gateway over Ethernet using an MQTT protocol. An MQTT broker can be deployed in the cabin management system controller, enabling the publish and subscribe mechanism with the gateway and the flight attendant panel. When the sensors send the status, it can be shown on the flight attendant panel, and any control from the flight attendant panel can be relayed to the actuators.
How an IoT-enabled subsystem helped OEM reduce cost?
One of the leading OEMs providing advanced aerospace solutions approached ACL Digital to develop an aircraft Wireless Cabin Control System (WCCS) to reduce overall weight and simplify the initial installation and configuration of the various cabin control components like lights, overhead bins, and passenger service units (PSU), ultimately reducing the installation labor costs. ACL Digital being a leading IoT solutions provider catering to the aviation industry helps address the challenges of aircraft manufacturers by providing smart aerospace industry solutions including cabin management systems, in-flight entertainment systems, aircraft structural health monitoring systems, and more.
Read our success stories to know how ACL Digital helps aviation companies to design and develop smart aerospace solutions using IoT technology.
Related Insights


