

Sanjaya Kumar Ojha
8 Minutes read
Network Slicing: An Emerging Paradigm in 5G Service Guarantee
The journey of wireless mobile technology from 1st Generation to the almost approaching 5th Generation has been nothing less than an adventurous and exciting one.
Let’s visit this exciting journey from 1G to 5G and understand the need for Network Slicing.
1st Generation :
1st generation mobile technology was introduced in 1980. With a speed of 2.4kbps, it allowed only voice call and that too in a specific province or country. It had poor voice quality, low battery life, large phone size and no security.
2nd Generation :
2nd generation mobile technology was introduced around 1991 which was based on GMS technology and digital signal, with 64 kbps. It enabled services like SMS and picture message. Though the quality is better than the 1G, but was not good enough in handling digital signal on weak signal level. 2G couldn’t handle little complex data, such as high quality of picture and small video.
2.5 Generation :
This was developed between 2G and 3G. This generation introduced GPRS and supported big images, emails, and web browsing with a speed of 64-144kbps.
3rd Generation :
The 3rd generation mobile technology was introduced with a speed of up to 2mbps. Its Multimedia services support along with streaming feature was much talked about. The supported handsets were typically called smart phones. Email communication became faster, and video and TV streaming capabilities were introduced. The major disadvantage was being too expensive to use data and as well as the handset.
4th Generation :
Presently 4th Generation of wireless mobile technologies is in use. It has high speed of data access with superior quality of digital streaming along with security. It supports a speed of up to 1Gbps and allows any time anywhere accessibility and reachability.
5th Generation :
We are heading towards a 5th Generation of mobile technology which will be more reliable, and will support better speed and better range. 5G is intended to provide complete wireless mobile technology, which supports Wireless World Wide Web (WWWW) methodology. It will enable ultra-high speed data transmission, larger phone memory along with clarity of voice and video on move. All in all 5G has the ability to redefine and change the meaning of cell phone usability. 5G supports the following:
- Virtually zero latency or in other wards faster response
- Speed up to 10Gbps
- Supports wide range of application
- Ubiquitous connectivity
- High reliability of communication
- Very high capacity of handling data
- Lower battery consumption
- Larger number of supporting device connectivity
5G is built to enable instantaneous connectivity to billions of devices, such as, the Internet of Things (IoT) for a truly connected world.
Three broad level categories of 5G key services are:
1. mMTC
Massive Machine Type Communications that aim to provide connectivity to a huge number of devices where traffic profile is typically a small amount of data comes sporadically. So, latency and throughput are not the concern. This revolutionises modern industrial processes and applications with respect to agriculture, manufacturing and business communications.
Use cases of mMTC- IoT, intelligent traffic management, massive manufacturing equipment and smart city.
2. URLLC
Ultra Reliable Low Latency Communications that support critical mission such as real-time control of devices, industrial robotics, vehicle to vehicle communications and safety systems, autonomous driving and safer transport networks. Low latency communications also enables and ensures that remote medical care, procedures, and treatment.
Use cases of URLLC- Automotive for intelligent transportation, industrial automation and remote health care.
3. eMBB
Enhanced mobile broadband for providing significantly faster data speeds, greater capacity and keeping the world connected. Fixed wireless internet access for homes, outdoor broadcast applications without the need for broadcast vans and greater connectivity for people on the move are some of the new applications that 5G will be able to support.
Use cases of eMBB- Fixed wireless access that connects home and business with 5G.
Some of the performance parameters of various 5G services are as mentioned below:
- Peak data rate, uplink 10 Gbps and downlink 20Gbps
- Peak spectral efficiency, uplink 15bps/Hz and downlink 30bps/Hz
- Data transmission latency for URLLC scenario is 1ms and for eMBB scenario is 4ms
- Connection density up to 10,00,000 per square kilometre in mMTC usage scenario
- Mobility interruption time is 0ms
- High speed mobility supported. The speed of vehicular movement supports from 120km/h to 500km/h
- High energy efficiency: Energy efficiency of network and device can be related to efficient data transmission in a loaded usage scenario and low energy consumption in idle condition
- Bandwidth of at least 100MHz and up to 1GHz for higher frequency bands
But the crucial question is how to achieve above 5G key services?
One of the emerging paradigms in 5G services is Network Slicing. Below are some of the silver bullet techniques to achieve 5G services:
New Radio (NR)
Use of small cells at new millimetre wave where connection range is very small but helps to achieve uninterrupted connection by deploying a cluster of small cell towers.
Cloud Native Core Network
5G core network has been redesigned by separating control plane and user plane by introducing micro service architecture that integrates with cloud service.
Network Functions Orchestration
Enables micro services, which helps in instantiating NFs at any desired location within the operator’s cloud. NFs are required to enable the speed efficiency and agility to support new business applications.
Network Slicing
A key paradigm in 5G architecture that enables 5G to achieve ultra-low latency, high speed and security services. It is a smart way of segmenting network for a specific service or industry or application. This enables and accelerates digital transformation through 5G.
This crucial feature of 5G system allows partitioning of a single network into several numbers of isolated logical (virtualized) networks, where each slice is being optimized for a dedicated service, to a specific End-User (UE) by their respective SLA Policy.
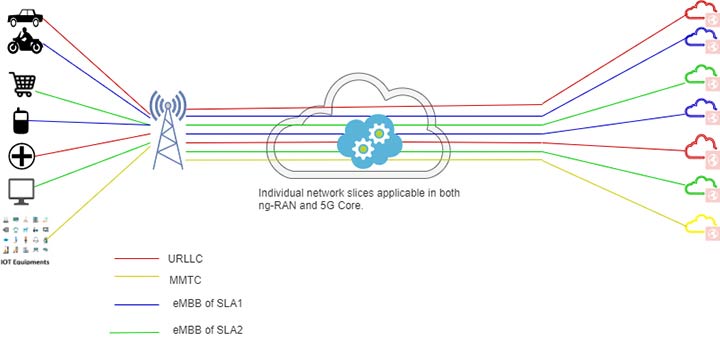
Network Slicing changes the economics of the connectivity business by not only optimizing customer service delivery, but also enabling different industries landscape to rapidly deploy their services. These landscapes are innovatively sliced from global general operational service provider infrastructure into a small number of service specific virtual network dedicated slices. It enhances Quality of Service (QoS) drastically by offering customers and industries a unique service “Network-as-a-Service (NaaS)” for implementing dedicated, and customized virtual end-to-end networks.
5G Network Slicing technology is being spanned across next generation New Radio (NR) and New Generation Core (5GC). Network Slicing is a 5G cutting edge technology, which creates multiple independent virtualized end-to-end network, providing flexibility to serve industry or business related service of high speed broadband (eMBB), advance emergency services (URLLC) and machine to machine communication (mMTC) cost-effectively, where the traditional network technology failed to achieve above services.
Based on the demand and evolution of technology the key components of network slicing are micro-service architecture and orchestration. Each slice in the technology is created dynamically in a group of related network functions to serve a specific purpose to dedicated business requirement without interfering with the other slices. It means slices are completely isolated and independent of each other.
Above image is an example of network slices of URLLC, eMBB and mMTC being created dynamically and dedicated to respective business services without any interference from the other slices.
This technique has lowered the risk of introducing & running new services as different services can be launched on new isolated slice. Each slice typically contains orchestration capabilities, which can easily be controlled by operator based on service level agreement.
Each dedicated isolated slice will be provided a network policy to achieve SLA, such as throughput, latency, jitter, loss, and availability along with energy-efficiency as well as cost-efficiency based on business goal. Owing to its flexibility, scalability, controllability and spanning across new generation of RAN & 5G core, Network Slicing provides guaranteed 5G key services which are being depicted above.
Network Slicing maintains security and privacy on its own. Security aspects are,
- Slice security: In case of any cyber-attacks, it only affects the specific slice and other services remain unaffected
- Slice privacy: Individual slice information is not shared among other slices
To summarize, Network Slicing is an effective technique to provide Zero Latency, Data Security, Energy Efficiency, Reachability and Guaranteed QoS with defined throughput.




