
Kumarappan Subramanian
5 Minutes read
Vibe Coding & AI‑Driven Development: Work with AI, Not Alone
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming how developers build software. Rather than replacing developers, AI is becoming a partner that enhances creativity, productivity, and efficiency. This concept, known as Vibe Coding, focuses on working in a natural flow, where developers collaborate with AI tools to streamline repetitive tasks and focus on innovation. This blog explores what vibe coding is, how AI is reshaping software development, the benefits of adopting this approach, the challenges organizations should be aware of, and the future landscape of AI-assisted coding.
The traditional software development process often requires significant effort in debugging, boilerplate coding, and researching solutions. Developers can lose focus when switching between problem-solving and routine tasks. With the emergence of AI-driven coding assistants, the process has undergone a significant shift. Developers now have tools that act as intelligent partners, supporting them in real time. This shift is not about replacing human expertise but about enabling developers to work more effectively and remain in a productive flow.
What Is Vibe Coding?
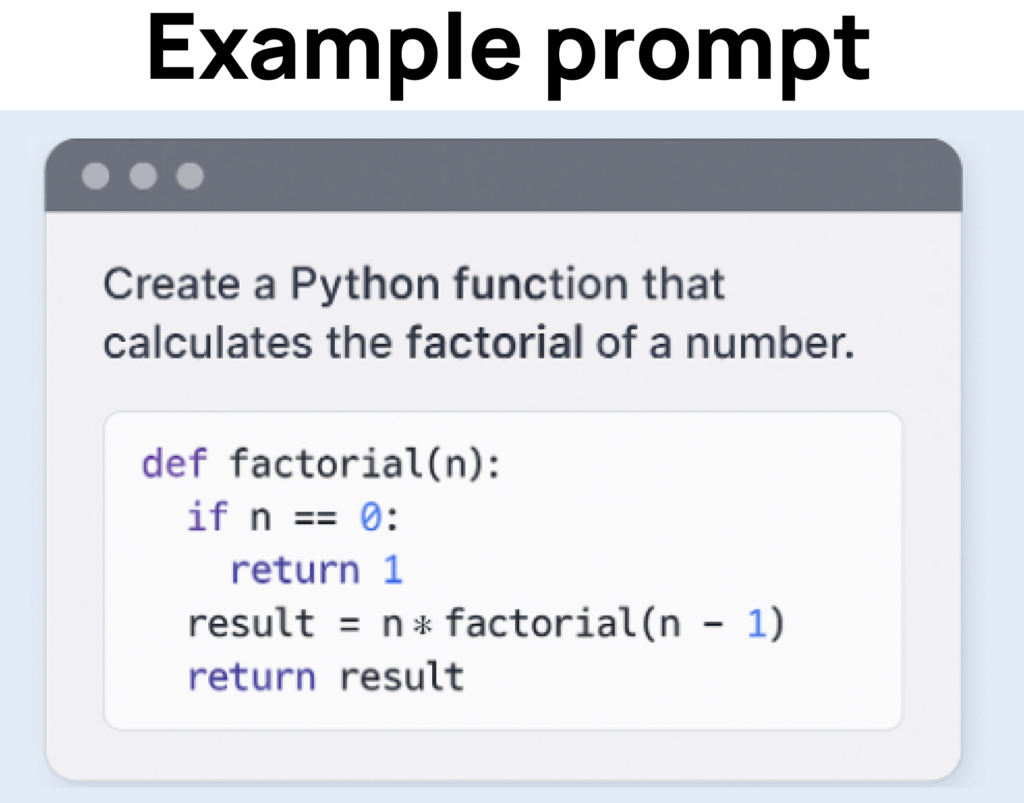
Vibe Coding is a new way of programming where the developer doesn’t write every line of code. Instead, they provide natural language prompts (in plain English instructions), and the AI generates most of the code. The process is fast, iterative, and relies on accepting and refining AI-generated output rather than manually building everything from scratch.
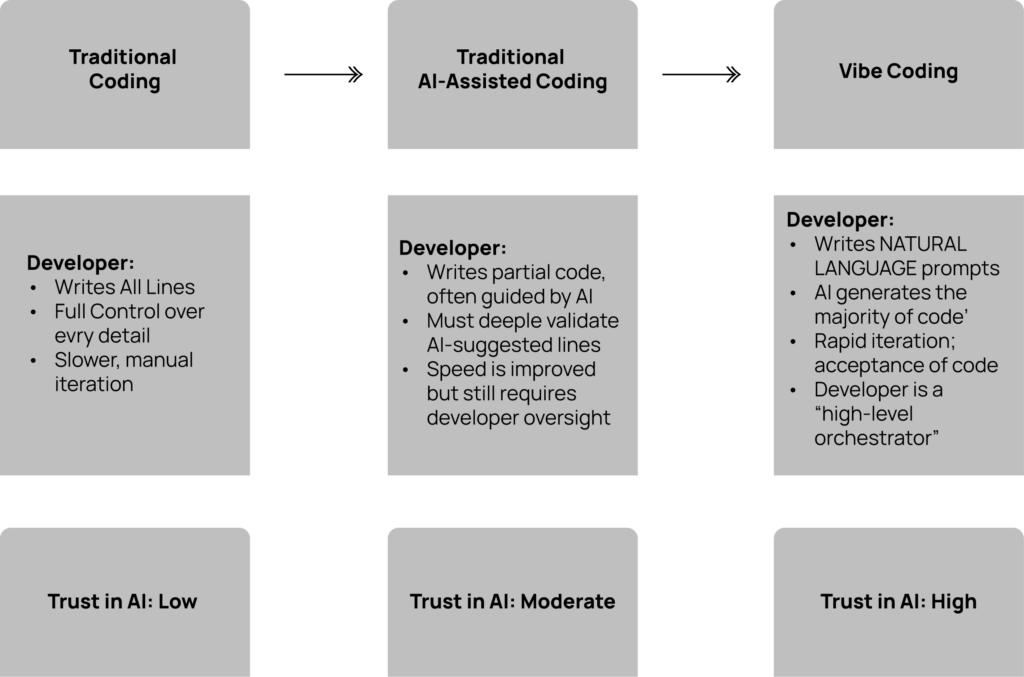
In this model, the developer’s role shifts from being a “line-by-line coder” to a high-level orchestrator—someone who guides the AI, sets direction, and ensures the final solution works as intended. Unlike traditional coding or AI-assisted coding, vibe coding makes developers place greater trust in AI, since the machine produces much of work while the human steers the process instead of controlling every detail.
How AI Is Shaping Development
AI technologies are reshaping software engineering practices by:
- Automating repetitive tasks such as writing boilerplate code and test cases.
- Detecting and fixing errors earlier in the process.
- Providing contextual explanations to accelerate learning for new developers.
- Assisting with design and architecture through intelligent recommendations.
By handling routine tasks, AI enables developers to focus on design, strategy, and problem-solving, thereby accelerating both the speed and quality of delivery.
Faster Prototyping in Vibe Coding
What Makes Vibe Coding Ideal for Rapid Prototyping?
Vibe coding does note replace full-scale production development, but it transforms how teams prototype, validate ideas, and test new features. The speed at which large language models (LLMs) can produce code is staggering—often up to ten times faster than even the most skilled developers. For early-stage projects or low-risk experiments, vibe coding lets you move from idea to working prototype almost instantly.
Speed & Efficiency Gains
Traditional coding often means extended handoffs between designers and developers, with days or weeks spent waiting for feedback. Vibe coding eliminates much of that friction by turning ideas into working code within minutes.
Key Benefits:
- Order of Magnitude Faster – LLMs generate usable code up to ten times quicker than humans.
- Cut Development Time in Half – Teams report cutting prototyping cycles by 50%.
- Accelerated Validation – What once took weeks can now be tested in days or even hours.
How Vibe Coding Transforms the Workflow
From Idea to Prototype
Instead of hand-coding every detail, developers can now describe what they want in plain English and let AI generate the initial code draft.
The Workflow:
- Describe – Write a clear prompt describing the desired feature.
- Generate – The AI produces the code in seconds.
- Test – Run the prototype immediately.
- Iterate – Refine by adjusting prompts and adding feedback.
This not only makes the process faster, but it also opens the door for non-developers to contribute actively.
Accessibility Revolution
Democratizing Development
With vibe coding, you don’t need to be a professional developer to create prototypes. Product managers, designers, and even marketing teams can now bring ideas to life without heavy technical barriers.
Who Can Prototype Now:
- UX Designers – Build and test layouts without waiting for developers.
- Product Managers – Validate features directly.
- Entrepreneurs – Turn ideas into working demos fast.
- Marketing Teams – Experiment with features for campaigns.
Iterative Design Culture
Rapid Feedback Loops
Prototyping with vibe coding encourages agile experimentation. Instead of waiting weeks for developer builds, teams can make real-time adjustments.
Comparison:
- Traditional: Design → Development → Testing → Feedback → Rework (weeks)
- Vibe Coding: Prompt → Generate → Test → Refine (minutes)
Vibe Coding in Practice: Real-World Examples
So far, we’ve explored what vibe coding is and why it matters. But what does it actually look like in action? Let’s walk through a concrete example where a developer uses vibe coding to build a task management app. You’ll see how the workflow plays out step by step: Prompt → AI Output → Human Refinement.
Example: Building a Task Management App
Phase 1: Initial Prompt & AI Output
Human Prompt:
“Create a task management app with user login, task lists, and a due date filter. List the pages and entities before generating code.”
AI Output:
- Pages: Login, Dashboard, Task List, Settings
- Entities: Users, Projects, Tasks, Comments
- Features: Authentication, CRUD operations, filtering, notifications
Human Refinement:
The developer reviews the plan and realizes project collaboration is missing. They refine the prompt:
“Include team member assignment and project sharing capabilities.”
Phase 2: Database Schema Generation
Human Prompt:
“Generate a Postgres schema with tasks, users, and permissions. Include constraints and indexes.”
AI Output:
- User authentication tables
- Task management schema
- Permission and role systems
- Optimized indexes for performance
Human Refinement:
The developer spots a gap: the code does not handle deletion rules. They say, “Add ON DELETE CASCADE for user-task relationships and clean up orphaned projects.”
Phase 3: Incremental Feature Addition
Human Prompt:
“Add email notifications when tasks are overdue. Show me the code changes only.”
AI Output:
- Email service integration
- Notification scheduling
- Template generation
- User preference handling
Human Refinement:
After testing, the developer notices that the unsubscribe options are missing. They follow up:
“Add unsubscribe links to all email notifications and a user preference dashboard.”
Best Practices for Rapid Prototyping
Choose the Right Tool
- Cursor – AI-assisted coding with chat features.
- Windsurf – VS Code fork with smooth AI integration.
- Replit – Cloud-based, great for quick testing.
Write Clear Prompts
- Instead of “Make a button,” say:
“Create a blue ‘Submit’ button aligned to the right.”
Test Immediately
- Run prototypes immediately after the system generates code.
Iterate with Feedback
- Collect input from users, and then refine the prompts accordingly.
Integration Benefits
Many vibe coding platforms connect directly with design tools like Figma, making the design-to-code workflow seamless. You can upload designs and instantly generate functional components.
When to Use Vibe Coding for Prototyping
Best Scenarios:
- Low-stakes experimentation
- Early concept validation
- Cross-functional team collaboration
- Rapid user testing cycles
- Startup MVPs
Success Factors:
- Write clear, specific prompts.
- Embrace iteration over perfection.
- Keep focus on user feedback.
- Balance speed with quality (it’s for validation, not production).
Significant Challenges in Vibe Coding
Vibe coding—where developers collaborate with AI tools to generate, refine, and ship code faster—feels like the future of software development. But like any shift this big, it doesn’t come without risks. While the promise of speed, efficiency, and creativity is real, there are also critical challenges that developers, teams, and organizations need to keep an eye on.
Let’s break down the three big challenges in vibe coding—and why they matter for the future of tech.
Intellectual Property Ownership Challenges
Ownership Ambiguity
One of the thorniest issues in AI-assisted coding is who owns the code. With vibe coding, attribution and originality aren’t always clear:
- Code Attribution: If AI generates the code, who owns it—the developer, the company, or the AI vendor?
- Patent Strategy Shifts: As code becomes easier to generate, companies must rely on IP protection (such as patents and trade secrets) rather than solely on technical complexity.
- Copyright Complexity: Can AI be acknowledged as a creator? The debate is ongoing.
- Training Data Issues: Vast amounts of code, often with unclear licensing, train AI models, which makes the output legally murky.
Protection Strategies Needed
Patents are one option, but they’re not enough. A multi-layered IP strategy—mixing utility patents, design patents, copyrights, trademarks, and trade secrets—is essential for organizations navigating this new era.
Dependency on Closed AI Models
Vendor Lock-in Risks
Relying on a single provider for vibe coding tools (like OpenAI, Anthropic, or GitHub Copilot) can create dangerous bottlenecks:
- Single Point of Failure: If the provider goes down, your workflow also comes to a halt.
- Cost Volatility: Sudden pricing changes can significantly impact budgets.
- API Limitations: Sticking to one ecosystem limits flexibility. Using multiple providers reduces the risk.
Technical Dependencies
Beyond business risks, there are technical trade-offs too:
- Black Box Problem: Most AI models do not explain how they generate code.
- Version Control Issues: The same prompt might produce different outputs as models evolve.
- Integration Challenges: AI code does not always play nicely with existing pipelines, security checks, or DevOps processes.
Skill Erosion Among Developers
Core Programming Skills Decline
Perhaps the most subtle, but critical challenge: developer skills may weaken over time.
- Problem-Solving Atrophy: Relying too heavily on AI can dull debugging and problem-solving instincts.
- Understanding Gaps: Developers may struggle to maintain complex systems without hands-on coding practice.
- Junior Developer Impact: New coders might never fully develop fundamentals if they start by “vibing with AI” instead of learning from scratch.
Long-term Maintenance Issues
AI-generated code can save time today, but it may cost more tomorrow:
- Technical Debt Accumulation: Non-standard or unclear code leads to future headaches.
- Debugging Difficulties: Troubleshooting AI-written code can be more challenging without a complete comprehension.
- Quality Assurance Challenges: Without rigorous review, inconsistency creeps in.
Getting Started with Vibe Coding
Organizations and individuals can begin adopting vibe coding practices by:
- Selecting AI coding assistants such as GitHub Copilot, ChatGPT, or similar tools.
- Starting with small, well-defined use cases such as documentation, bug fixing, or boilerplate generation.
- Encouraging developers to review and validate all AI suggestions.
- Promote a culture that treats AI as an assistant, not an authority.
This approach strikes a balance between efficiency and accountability, ensuring the sustainable adoption of the solution.
The Future of AI-Assisted Coding
The future of Vibe Coding points to a world where AI and humans work even more closely together to create software. Developers will move beyond just prompting AI to fully shape automated systems that can manage the entire development cycle. AI will generate not only code but also pipelines and workflows, making the software process more autonomous.
We’ll also see a merging of different approaches—low-code, no-code, and pro-code—so that both beginners and experts can work within the same flexible environment. Another important direction is the rise of green software development, where coding practices focus on energy efficiency and sustainability.
As new technologies like quantum computing and edge computing become mainstream, vibe coding will adapt to support these advanced lifecycles. Finally, the most exciting part of this future is human–AI co-evolution. Instead of humans merely using AI as a tool, both will grow and improve together, creating a more creative, efficient, and sustainable approach to building software.
Conclusion
Vibe coding is reshaping how developers approach software creation—turning ideas into prototypes faster, encouraging collaboration, and weaving AI into everyday workflows. While it comes with challenges like IP ownership, over-reliance on closed models, and skill erosion, the benefits of speed, flexibility, and innovation outweigh the risks when paired with the proper guardrails. By combining AI-powered assistance with human oversight, teams can ensure both velocity and quality. The journey ahead isn’t about replacing developers but about empowering them with more innovative tools.
The future of coding isn’t man versus machine—it’s man and machine, building together.
Related Insights





How Generative AI is Transforming Project Risk Management

